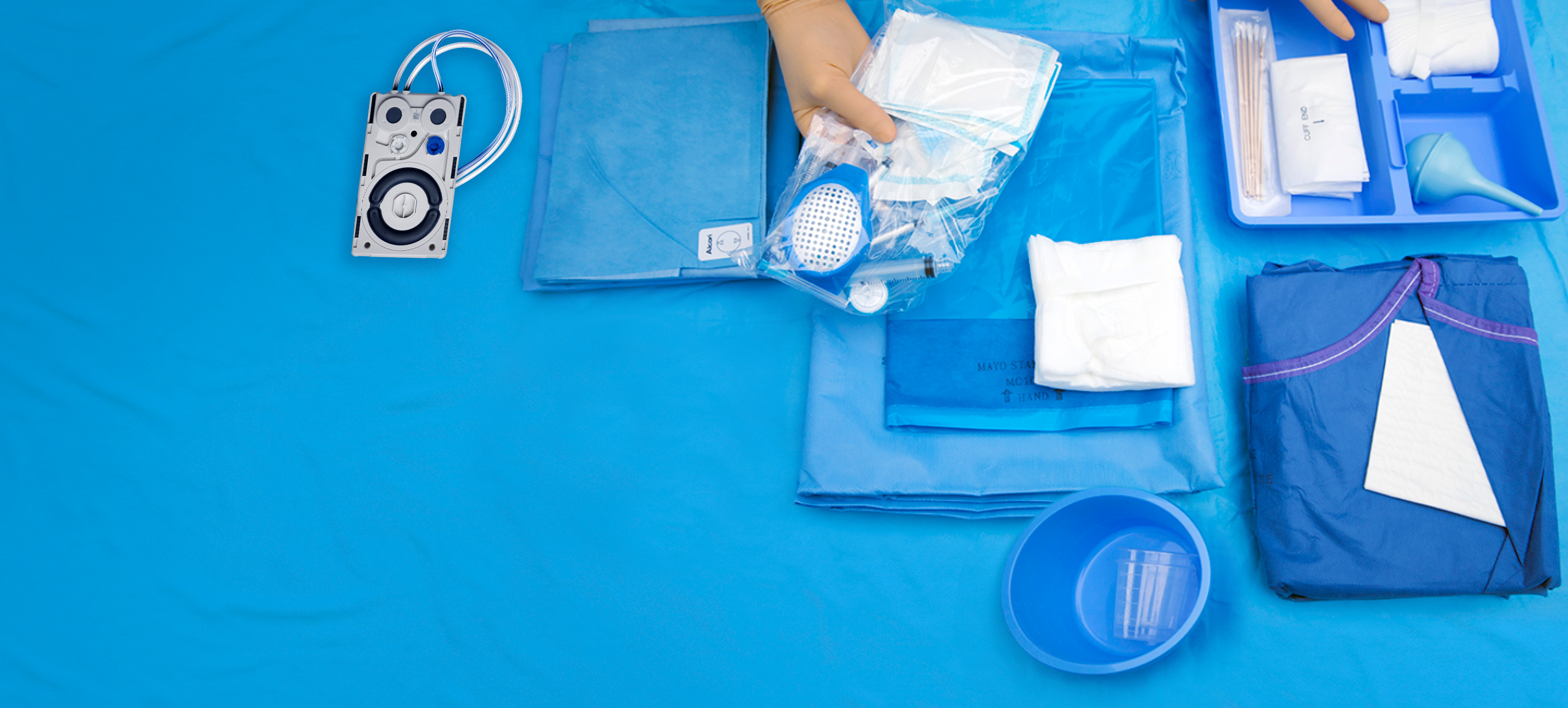
Disposables
Empowering Cataract Procedures
Disposables
Empowering Cataract Procedures
Alcon Custom-Pak®
Designed to maximise surgical efficiency and ensure that surgeons receive their preferred products.
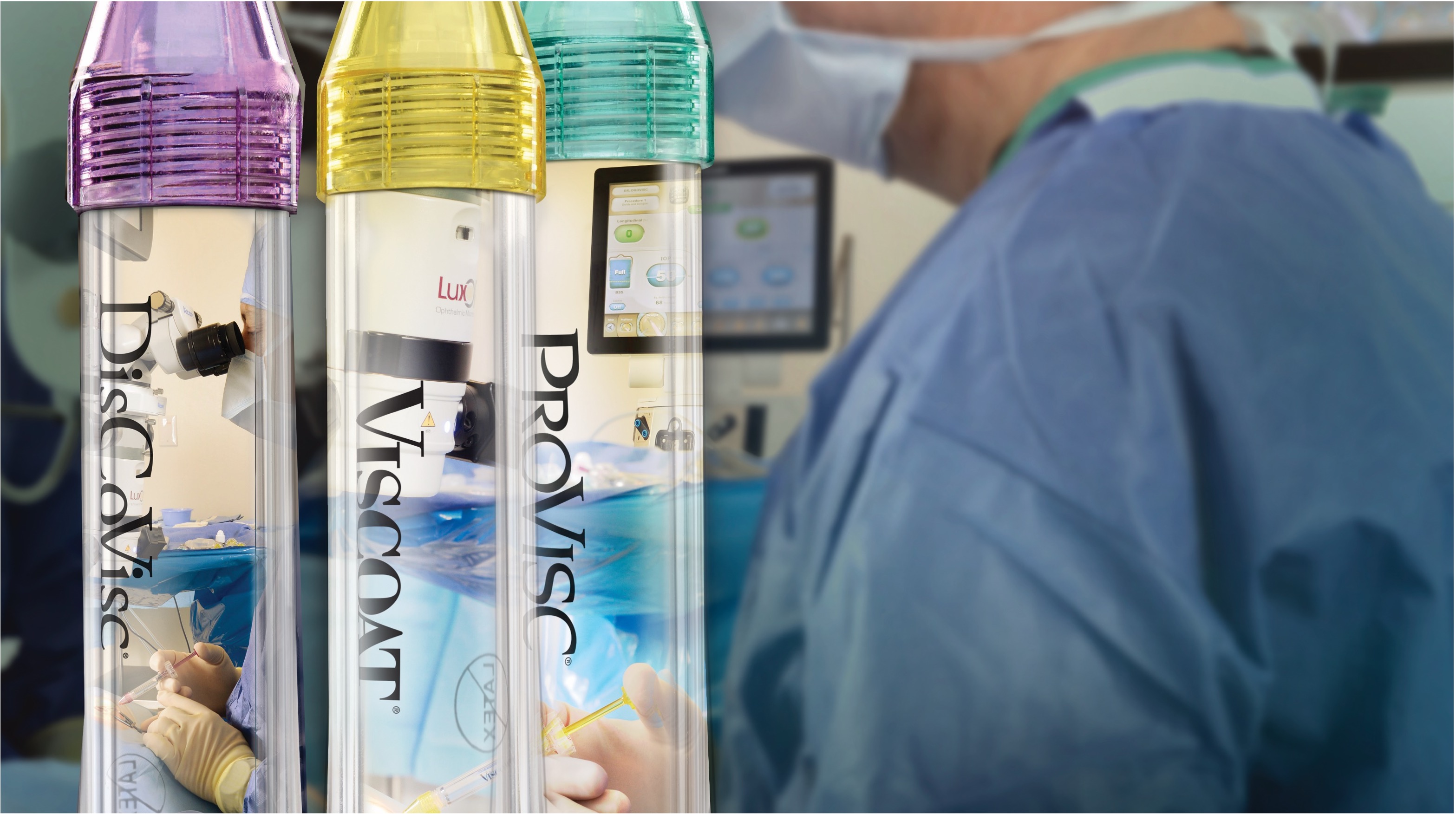
Ophthalmic Viscosurgical Devices (OVDs)
Alcon OVDs are designed with specific physicochemical properties to optimise every step of the procedure.
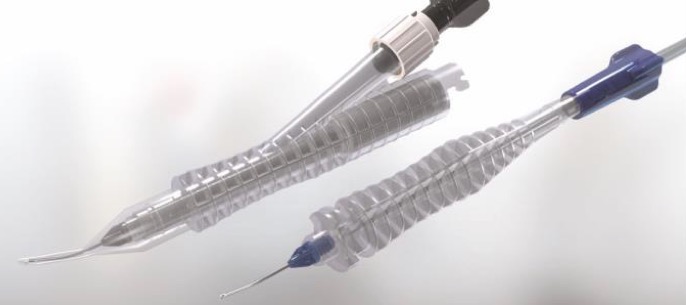
Intrepid®
Make your phaco procedures more effective by merging the technology of Centurion® Vision System with the effectiveness of INTREPID® Phaco Tips.
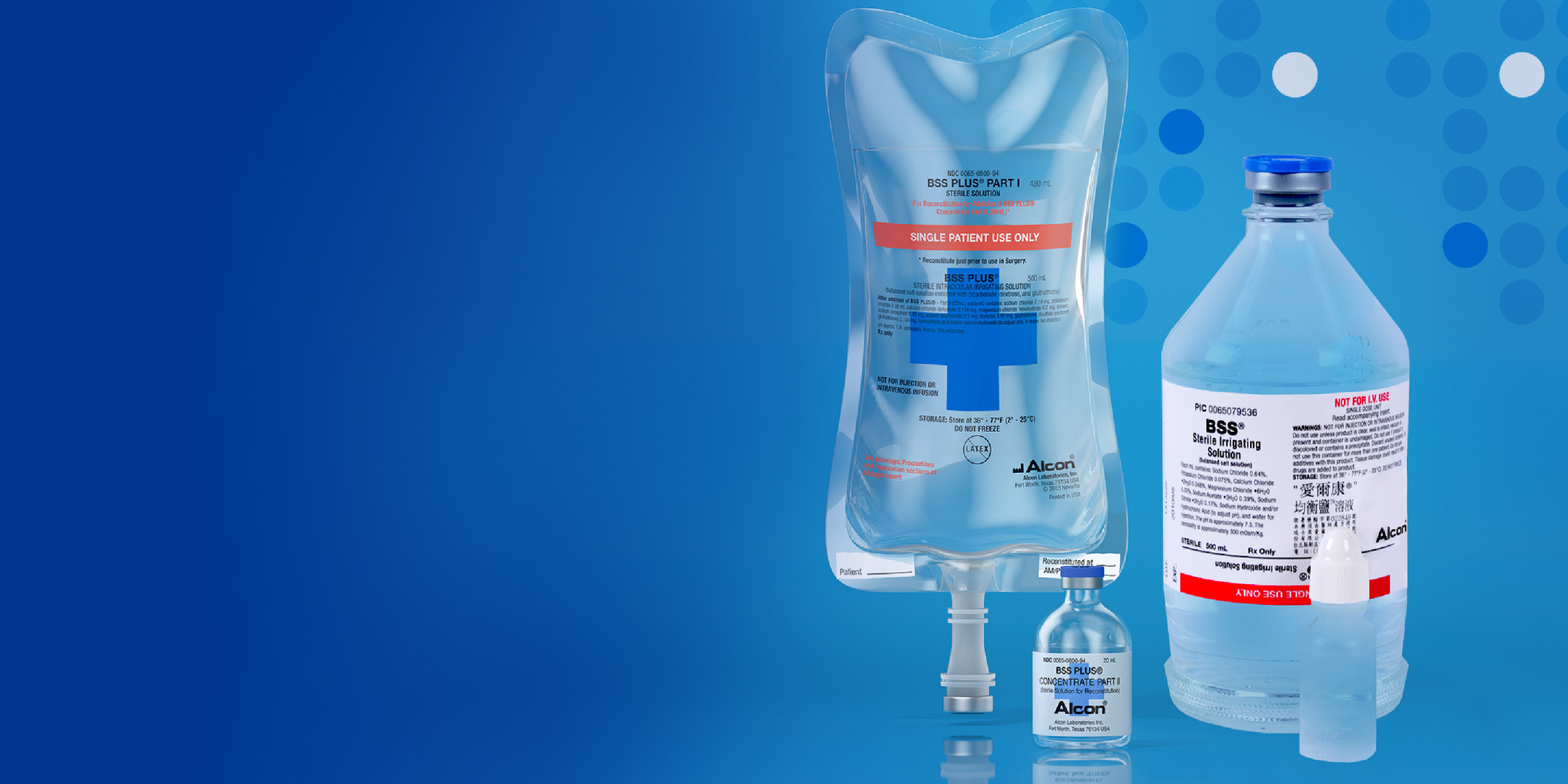
BSS® / BSS PLUS®
Intraocular Irrigating Solutions
Alcon Experience Academy
For relevant training content from industry thought leaders
©2022 Alcon Inc. 08/22 US-CPP-2200009



